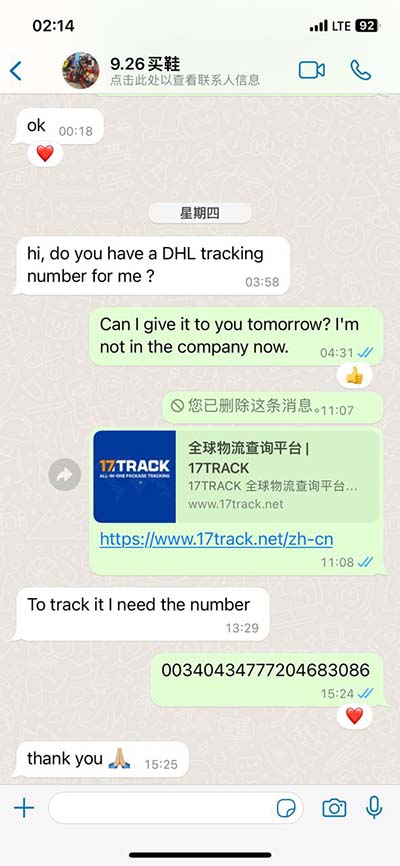
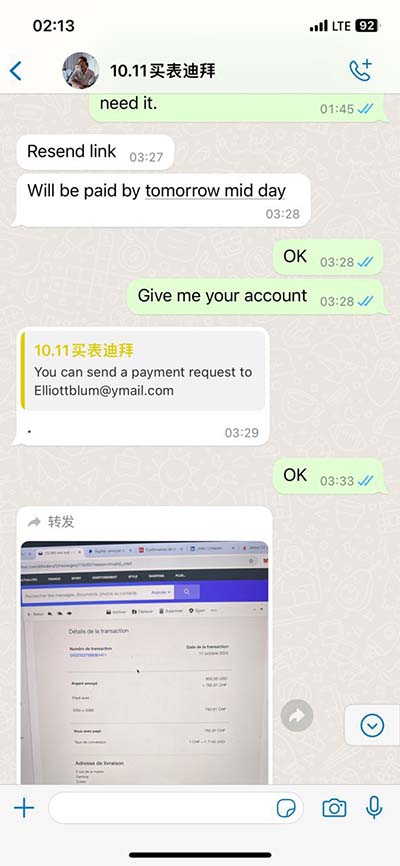
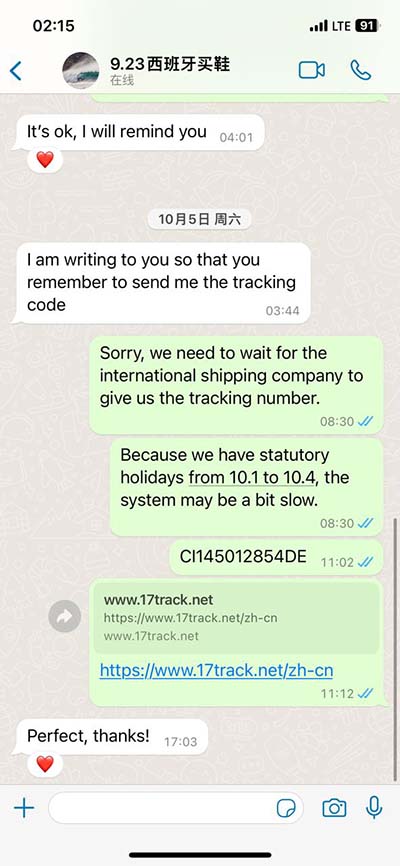
replication vs transcription vs translation What's the difference between Transcription and Translation? Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. . Uzņēmums organizē ceļojumus uz gandrīz 90 galamērķiem 38 pasaules valstīs, ieskaitot Turciju, Grieķiju, Spāniju, Ēģipti, Apvienotos Arābu Emirātus un Taizemi. Coral Travel Latvia - Tas ir pieredzes, starptautisko zināšanu un spēka apvienojums, kas padara ceļošanas procesu ērtu un neaizmirstamu.
0 · transcription vs translation diagram
1 · transcription vs translation biology
2 · transcription vs dna replication
3 · replication vs transcription translation
4 · does transcription occur before translation
5 · dna replication vs protein synthesis
6 · dna replication vs gene expression
7 · compare and contrast transcription translation
Crafty Chandler. 48-50 Bold Street - Liverpool. Bar. • British. • Pub. 70/100. Recommended by 2 people. +2. Unclamed activity. SEE ALL (+19) Browse the menu. Reviews Call Timetable Make a reservation Order online Add photo Share Map Ratings. What's your favorite Crafty Chandler's dish? Ratings and reviews. 70.
Here’s a handy chart you can look at if you need to remember the differences between transcription, translation, and replication: Aug 9, 2022 The purpose of transcription is to make RNA copies of genes. The purpose of translation is to synthesize proteins for cellular functions. Translation produces proteins, .What's the difference between Transcription and Translation? Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. .
DNA serves as the molecular basis of heredity through replication, expression, and translation processes. Replication creates identical DNA strands, while transcription converts DNA into .
Translation of mRNA. Cell cycle. This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Transcription Translation and Replication essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to .
Transcription Prokaryotic. Review flow of information in cell DNA-----> RNA ----->Protein replication transcription translation. I. Genetic Code: one to one relationship between .

In prokaryotic cells, transcription (DNA to mRNA) and translation (mRNA to protein) are so closely linked that translation usually begins before transcription is complete.There are three key differences between replication and transcription: RNA molecules are much shorter than DNA molecules; only a portion of one DNA strand is copied or transcribed to make an RNA molecule.
Retroviruses such as HIV use this method of replication. This process produces altered DNA, which can be incorporated directly into a host cell, allowing rapid reproduction. . Table 1: The differences between translation .Replication vs Transcription; What Is Replication? What Is Transcription? Conclusion; DNA replication is defined as the process involved in obtaining two daughter strands where each strand contains half of the DNA double helix. .
Introduction. DNA replication and transcription are fundamental processes that occur within living organisms. They play crucial roles in the transfer of genetic information and are essential for the proper functioning and development of all living organisms.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like where replication occurs, where transcription occurs, where translation occurs and more. The production of proteins is completed through two processes: transcription and translation. Transcription and translation take the information in DNA and use it to produce proteins. Transcription uses a strand of DNA as a template to build a molecule called RNA. The RNA molecule is the link between DNA and the production of proteins.The balance between replication and transcription is akin to maintaining both the master archive and the active workshop. Replication ensures that the genetic archive remains intact and unaltered for future generations of cells, preserving the genetic identity. Meanwhile, transcription allows for flexibility and responsiveness, enabling your .
The processes of transcription and translation are collectively referred to as gene expression. Section 13.2: DNA Replication The DNA replication process is semiconservative, which results in two DNA molecules, each having one parental strand of . S.N. Character: DNA Replication: Transcription: 1. Definition: DNA replication is the process of making new copies of DNA. Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied (transcribed) to RNA.Transcription, Translation and Replication. DNA, RNA and protein synthesis. The genetic material is stored in the form of DNA in most organisms. In humans, the nucleus of each cell contains 3 × 10 9 base pairs of DNA distributed over 23 pairs of chromosomes, and each cell has two copies of the genetic material. This is known collectively as .
Because the RNA that is synthesized is a complementary copy of information contained in DNA, RNA synthesis is referred to as transcription. There are three key differences between replication and transcription: RNA molecules are much shorter than DNA molecules; only a portion of one DNA strand is copied or transcribed to make an RNA molecule. Replication is known to be semiconservative as the original DNA (the parent strand) splits to make a new strand, while retaining the parent strand. Replication in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is quite similar. The difference . DNA replication occurs in preparation for cell division, while transcription happens in preparation for protein translation. DNA replication is important for properly regulating the growth and division of cells. The DNA will . SB2.a-Replication VS Transcription VS Translation SB2.a-Replication VS Transcription VS Translation. Loading ad. Mrs. Rondina. Member for 3 years 7 months Age: 14+ Level: 9TH, 10TH. Language: English (en) ID: 1589715. 31/10/2021. Country code: US. Country: United States. School .
The translation follows the transcription up: in the cytoplasm, more precisely in ribosomes located in polyribosomalcomplexes or in the rough endoplasmatic reticulum, a rRNA unit binds a single-strand mRNA chain, which enhosts the genetic code as mirror of the DNA template. tRNA units carry aminoacids (each tRNA bindt to one specific aminoacid . A gene is a sequence of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule that codes for the production of a specific sequence of amino acids, that in turn make up a specific polypeptide (protein); This process of protein synthesis occurs in two stages: . Transcription – DNA is transcribed and an mRNA (messenger RNA) molecule is produced; Translation – mRNA is .10.3 DNA Replication; 11. Transcription and Translation. 11.1 Transcription; 11.2 Protein Translation; 12. Gene Regulation and the Cell Cycle. . Unlike DNA synthesis, which only occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, transcription and . 4. Leading strand: Strand that can continuously be synthesized from the 5’ → 3’ direction 5. Lagging strand: Strand that cannot be continuously synthesized from 5’ → 3’ and is instead synthesized in fragments and requires a little help from ligase. Key enzymes: 1. Helicase: Unzips the DNA so the other enzymes can access the nucleotide sequence
The rate at which transcription and translation occur drive evolution, along with the chosen alternative splicing of the messenger RNA. As new genes are expressed and frequently expressed, new proteins are made and new .replication; translation b. translation; transcription c. transcription; translation d. replication; transcription Explain how the process of transcription and translation makes proteins from DNA. Use the following terms in your explanation: template strand, RNA polymerase, nucleus, mRNA, cytoplasm, ribosome, tRNA, amino acid, peptide bond .
carteira prada usada
choose the site nearest you: elko; las vegas; reno / tahoe
replication vs transcription vs translation|dna replication vs gene expression